ITSM SELF SERVICE PORTAL
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, efficient and streamlined IT service management (ITSM) is crucial for organizations to maintain their competitive edge. One of the significant innovations in ITSM is the advent of self-service portals.
These portals empower users to independently resolve their IT-related issues, leading to improved efficiency, reduced workload for IT teams, and enhanced user satisfaction. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of ITSM self-service portals, explore their evolution, and highlight the numerous benefits they bring to organizations.
Evolution of ITSM Self-Service Portals
The journey of ITSM self-service portals began with traditional help desks and service desks, where users had to communicate their issues via phone calls or emails, and IT personnel would subsequently resolve them. However, this process was time-consuming and often led to delays in issue resolution. As technology progressed, organizations realized the need to offer users a more efficient and convenient way to access IT support.
Early iterations of self-service portals offered basic features like FAQs and knowledge bases, enabling users to find solutions to common issues independently. Over time, these portals evolved to incorporate more advanced features such as automated request forms, live chat support, and knowledge articles. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning further elevated the capabilities of self-service portals, enabling predictive issue resolution, personalized recommendations, and intuitive user interfaces.
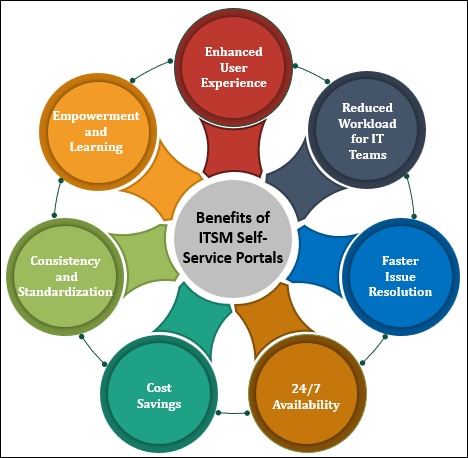
Benefits of ITSM Self-Service Portals
- Enhanced User Experience: Self-service portals empower users to resolve their issues at their convenience, eliminating the need to wait for IT personnel. Users can access knowledge articles, step-by-step guides, and video tutorials, enabling them to troubleshoot problems on their own. This leads to a significant improvement in user experience and satisfaction.
- Reduced Workload for IT Teams: With users being able to resolve routine issues independently, IT teams can focus on more complex tasks and strategic initiatives. This results in improved productivity and efficiency, allowing IT personnel to allocate their time and resources more effectively.
- Faster Issue Resolution: Self-service portals provide users with instant access to solutions, reducing the time taken to resolve IT-related problems. This swift issue resolution minimizes downtime and disruption to business operations, ultimately leading to increased organizational agility.
- 24/7 Availability: Self-service portals are accessible round-the-clock, enabling users to seek assistance at any time, regardless of business hours. This is particularly beneficial for global organizations with users in different time zones.
- Cost Savings: By promoting self-help and reducing the dependency on IT support staff, organizations can achieve substantial cost savings. The need for additional staffing to manage support requests diminishes, and resources can be redirected toward strategic IT initiatives.
- Consistency and Standardization: Self-service portals facilitate the dissemination of consistent and standardized information to users. This ensures that users receive accurate and up-to-date information, reducing the chances of errors and miscommunication.
- Data-Driven Insights: Self-service portals generate valuable data about user behavior, frequently encountered issues and popular solutions. Organizations can use this data to identify trends, optimize knowledge content, and make informed decisions to enhance their ITSM strategies.
- Scalability: As organizations grow, the demand for IT support also increases. Self-service portals are scalable solutions that can accommodate a growing user base without a proportional increase in support staff.
- Empowerment and Learning: Self-service portals encourage users to become more tech-savvy by exploring knowledge articles and attempting to troubleshoot issues independently. This empowerment enhances their digital skills and overall technological literacy.
Implementing a Successful ITSM Self-Service Portal Strategy
While the concept of an ITSM self-service portal is appealing, its successful implementation requires careful planning, strategy, and ongoing optimization. Here are
key considerations to ensure the effectiveness of your self-service portal:
- User-Centric Design: Prioritize user experience by designing the portal with a user-friendly interface, intuitive navigation, and a search functionality that helps users quickly find relevant information.
- Knowledge Management: Maintain an up-to-date and comprehensive knowledge base with clear and concise articles. Regularly review and update content based on user feedback and changing technology trends.
- User Training and Promotion: Educate users about the existence and benefits of the self-service portal through training sessions, email communications, and informative banners within the portal. Promote self-help as the preferred way of obtaining support.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor user interactions, feedback, and usage patterns to identify areas for improvement. Regularly analyze portal performance metrics to refine content, features, and functionality.
- Integration with ITSM Tools: Seamlessly integrate the self-service portal with your existing ITSM tools and workflows. This ensures that issues escalated from the portal to IT personnel are efficiently tracked and resolved.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Provide users with the ability to rate the usefulness of knowledge articles and submit feedback. This input can guide ongoing improvements and help identify gaps in the content.
- Artificial Intelligence and Automation: Leverage AI-powered chatbots and automation to provide instant responses to common queries and guide users through issue resolution processes.
- Change Management: Implement change management practices to smoothly transition users from traditional support methods to the self-service portal. Address user concerns and provide assistance during the initial stages.

Security and Compliance Considerations
Implementing an ITSM self-service portal brings about several security and compliance considerations that organizations must address to ensure the protection of sensitive data and adherence to industry regulations. While self-service portals offer numerous benefits, they also introduce potential risks, such as unauthorized access to information, data breaches, and exposure to confidential data.
- Authentication and Access Control: Organizations must implement robust authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users can access the self-service portal. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) can add an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access.
- Data Encryption: All communication between users and the self-service portal should be encrypted using secure protocols (e.g., HTTPS) to prevent eavesdropping and data interception. Additionally, data stored within the portal's databases should be encrypted to safeguard against potential breaches.
- Role-Based Access: Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that users can only access information and perform actions relevant to their roles within the organization. This prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data or making unauthorized changes.
- Audit Trails: Keeping a detailed record of user interactions and activities within the self-service portal can aid in monitoring for suspicious behavior, tracking changes, and investigating security incidents. Audit trails contribute to compliance with regulatory requirements and help organizations identify and mitigate potential threats.
- Data Privacy and Compliance: Organizations must ensure that the self-service portal aligns with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), depending on the nature of the data being processed. Users should have control over their data and the ability to manage their consent preferences.
Conclusion
ITSM self-service portals have come a long way from their humble beginnings as basic knowledge bases. Today, they stand as powerful tools that drive efficiency, user satisfaction, and operational excellence within organizations. By leveraging the benefits of self-service portals, businesses can transform their IT support functions, streamline issue resolution, and allocate resources more strategically. As technology continues to advance, self-service portals will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of modern ITSM practices, shaping the future of how organizations deliver IT support services.




