ITSM TOOLS COMPARISON
In the dynamic landscape of modern technology, Information Technology Service Management (ITSM) plays a critical role in ensuring smooth operations and customer satisfaction. ITSM tools have become indispensable for organizations seeking to streamline their IT services, enhance productivity, and improve service quality.
With a plethora of options available, choosing the right ITSM tool can be a daunting task. This comprehensive comparison aims to guide you through the key features, benefits, and considerations of various ITSM tools, enabling you to make an informed decision that aligns with your organization's needs.
Understanding ITSM and Its Significance
Before delving into the comparison, it's essential to grasp the concept of ITSM and its significance in modern business operations. ITSM encompasses a set of processes, policies, and tools designed to deliver, manage, and support IT services effectively. From incident and problem management to change and asset management, ITSM covers a wide range of activities aimed at ensuring the seamless functioning of an organization's IT infrastructure.
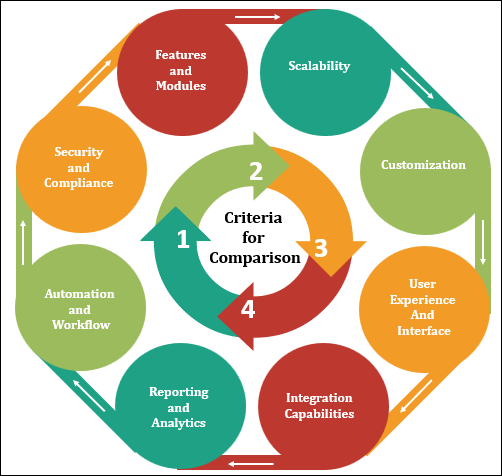
Criteria for Comparison
To conduct a meaningful comparison of ITSM tools, it's crucial to establish a set of criteria that evaluate their performance and capabilities. The following criteria will serve as the foundation for this comparison:
- Features and Modules: Analyzing the core features offered by each ITSM tool, including incident management, problem management, change management, asset management, knowledge base, and more.
- Scalability: Assessing the tool's ability to accommodate the growth of an organization's IT infrastructure and adapt to changing requirements.
- Customization: Examining the extent to which the tool can be tailored to match specific organizational processes and workflows.
- User Experience and Interface: Evaluating the tool's user-friendliness, intuitiveness, and overall interface design.
- Integration Capabilities: Investigating the tool's compatibility with other essential business systems and applications.
- Reporting and Analytics: Reviewing the tool's capacity to generate insightful reports and provide data-driven insights for continuous improvement.
- Automation and Workflow: Assessing the tool's automation features and its ability to streamline workflows for increased efficiency.
- Security and Compliance: Considering the security measures implemented by the tool and its adherence to industry standards and regulations.
Comparative Analysis of ITSM Tools
In this section, we'll compare a selection of popular ITSM tools based on the established criteria:
ServiceNow:
- Features and Modules: ServiceNow offers a comprehensive suite of modules, covering incident, problem, change, and asset management. Its extensive capabilities also include service catalog and request fulfillment.
- Scalability: ServiceNow is renowned for its scalability, making it suitable for both small businesses and large enterprises.
- Customization: The platform provides a high degree of customization, allowing organizations to tailor workflows and processes to their unique needs.
- User Experience and Interface: ServiceNow boasts an intuitive interface that enhances user experience, even for complex processes.
- Integration Capabilities: It offers robust integration with third-party applications, promoting seamless data exchange.
- Reporting and Analytics: ServiceNow excels in reporting and analytics, providing real-time insights for data-driven decision-making.
- Automation and Workflow: The tool's automation capabilities contribute to efficient process management and reduced manual intervention.
- Security and Compliance: ServiceNow adheres to stringent security standards and compliance regulations.
BMC Helix ITSM:
- Features and Modules: BMC Helix ITSM offers a comprehensive set of modules, including incident, problem, change, asset, and knowledge management.
- Scalability: The tool is designed to accommodate the growth of organizations, making it suitable for various business sizes.
- Customization: BMC Helix ITSM allows for process customization to align with specific business requirements.
- User Experience and Interface: Its user-friendly interface enhances usability and simplifies complex tasks.
- Integration Capabilities: The tool provides integration options for seamless data sharing with other systems.
- Reporting and Analytics: BMC Helix ITSM offers robust reporting and analytics features to track service performance.
- Automation and Workflow: It emphasizes automation, streamlining processes for improved efficiency.
- Security and Compliance: BMC Helix ITSM prioritizes security and compliance to protect sensitive data.
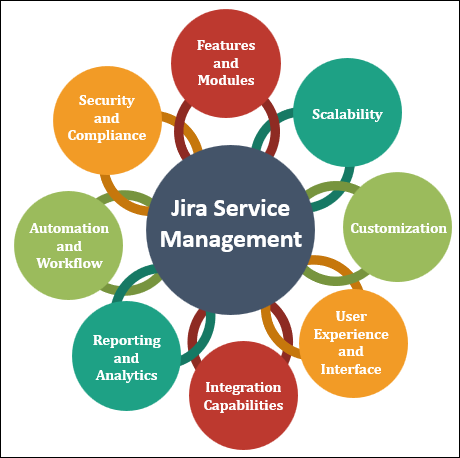
Jira Service Management:
- Features and Modules: Jira Service Management focuses on core ITSM modules like incident, problem, and change management, with advanced features for software development teams.
- Scalability: The tool is suitable for businesses of various sizes, but its strengths lie in software development-oriented processes.
- Customization: Jira offers customization to adapt its workflows to different business needs.
- User Experience and Interface: Known for its simplicity, Jira's interface appeals to teams with varying technical expertise.
- Integration Capabilities: Jira seamlessly integrates with a wide range of Atlassian and third-party tools.
- Reporting and Analytics: Jira provides basic reporting and analytics capabilities, with the option to enhance them through integrations.
- Automation and Workflow: Automation is a highlight, particularly for software development and DevOps practices.
- Security and Compliance: Jira adheres to security best practices but may require additional configurations for specific compliance needs.
Cherwell ITSM:
- Features and Modules: Cherwell ITSM offers standard ITSM modules, including incident, problem, change, and knowledge management.
- Scalability: The tool is suitable for businesses of various sizes, but its scalability might have limitations for larger enterprises.
- Customization: Cherwell provides a high degree of customization to match diverse organizational processes.
- User Experience and Interface: The tool focuses on user experience, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Integration Capabilities: Cherwell offers integration capabilities but might require additional configuration for certain integrations.
- Reporting and Analytics: Cherwell's reporting features are robust, providing insights for service improvement.
- Automation and Workflow: Automation capabilities enhance process efficiency and reduce manual intervention.
- Security and Compliance: Cherwell meets security standards, but specific compliance needs may require additional configurations.
Considerations for Selection
Choosing the right ITSM tool involves considering factors beyond feature comparison:
- Organizational Needs: Evaluate your organization's specific requirements and challenges.
- Budget: Consider the cost of the tool and potential return on investment.
- Ease of Implementation: Assess the tool's ease of deployment and onboarding process.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor's reputation, customer reviews, and support quality.
- Long-Term Strategy: Choose a tool that aligns with your long-term IT and business strategies.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving world of ITSM, selecting the right tool can significantly impact an organization's efficiency, service quality, and customer satisfaction. By comparing key features, scalability, customization, user experience, integration capabilities, reporting, automation, and security, organizations can make informed decisions that best suit their unique needs. Remember that the optimal ITSM tool aligns not only with current requirements but also with long-term business strategies, ensuring sustainable success in the dynamic IT landscape.




